Building the Deloitte Central European Middleware - ESB Project
The goal of the DCE Integration strategy is to build and standardize the process of data exchange between applications / systems working in CE. Replace the current "Point-to-point" communication model and individual solutions supporting data exchange between systems.
The Service Oriented Architecture - SOA model with a dedicated integration layer that physically implements data flows by acting as an "intermediary" between systems / data sources, allows to replace a system with a new one without the need to recreate all integrations.
This solution allows the flexible and effective development of integrations between the IT systems of Deloitte CE. Turn off/add/replace systems in the infrastructure without the need to disable the ongoing work of others.
The DCE middleware solution is built to support these integration strategy goals. Its name is Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) solution. ESB is using standard Azure integration services resources (Azure Logic Apps, Azure Service Bus, Azure API Management service, Azure Data-Factory, Azure SQL Server) to ensure the required logic and connectivity between systems. The solution is capable to connect on-premises, Deloitte Cloud, or vendor cloud solutions as well.
ESB offers a range of solutions and integration patterns, such as REST APIs, integrations based on PUBLISH-SUBSCRIBE model, or data transfer and transformation (ETL) through Azure Data Factory.
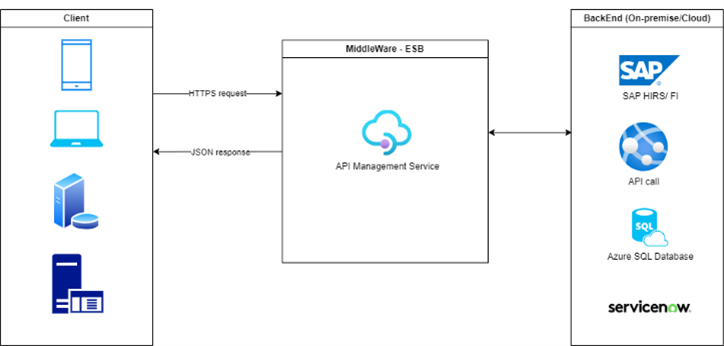
We are delivering a REST API-based solutions tailored to specific business data objects, with a continuously expanding scope via the ongoing major projects like Jupiter, PSA-Kantata, OnePlace etc.
Applications can make an API call to an endpoint delivered by Azure API Management Service for a specific resource using HTTPS protocol. This includes a specific HTTP request (GET, DELETE, POST, or PUT are the most common ones) and a URI—uniform resource identifier—, or endpoint, which specifies where the resource lives. Once the server validates the request, it returns information in JSON format, so that it’s easily readable / processable.
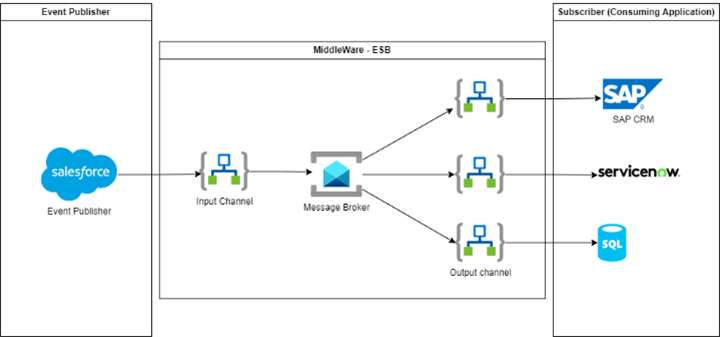
ESB is implementing a near-real time solution based on the Publish and Subscribe pattern to deliver platform events from Jupiter, or Kantata. We apply this model for those cases, where the source application provides access only to events (creation/change/deletion) for objects, and we do not have direct access to the data source. ESB provides a solution, which can deliver these changes to multiple applications parallel. Distribution of the events are happening based on a subscription. The changes are transferred to the consumers either via APIs, or database directly.
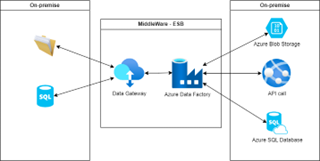
Beside integration ESB is providing functionalities for data migration and data load as well. Using Azure Data Factory we can access both on-premise and cloud resources and provide ETL capabilities. ETL (extract, transform, load) is a three-phase process where data is extracted from source system, transformed (cleaned, sanitized) and loaded into a target system. These capabilities are typically used during new system implementation, or during starting up a new integration based on pub-sub pattern.
For different phases of the projects ESB can provide these solutions through multiple environments supporting: Development, UAT and Cut-over activities. For none Production environments we can provide updates from test source systems (SAP Fi, SAP HR, Jupiter UAT etc.) . In these environments we are applying ESB changes continuously using CI/CD pipelines to support efficient testing. Update of the capabilities follows a monthly release schedule for Production.